멘토링
toString() 메소드의 내부를 살펴보자!!
langsamUndStetig
2022. 6. 17. 20:43
toString()은 Object 클래스의 메소드로 자주 오버라이딩하는 대상이다.
기존의 toString() 메소드 내부를 한번 살펴보자!
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
//Object 클래스의 메소드 getClass()
@IntrinsicCandidate
public final native Class<?> getClass();
// Class 클래스의 메소드 getName()
public String getName() {
String name = this.name;
return name != null ? name : initClassName();
}
//Integer 클래스의 static 메소드 toHexString(), hashCode가 int type이기 때문에 매개변수
public static String toHexString(int i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 4);
}
// toUnsignedString0 integer를 부호없는 값으로 나타낸다고 한다. 즉 예를 들어 3비트를 부호없이 나타낸다면 0~7 범위를 나타낸다.
/**
* Convert the integer to an unsigned number.
*/
private static String toUnsignedString0(int val, int shift) {
// assert shift > 0 && shift <=5 : "Illegal shift value";
int mag = Integer.SIZE - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(val);
int chars = Math.max(((mag + (shift - 1)) / shift), 1);
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] buf = new byte[chars];
formatUnsignedInt(val, shift, buf, chars);
return new String(buf, LATIN1);
} else {
byte[] buf = new byte[chars * 2];
formatUnsignedIntUTF16(val, shift, buf, chars);
return new String(buf, UTF16);
}
}byte[] a = new byte[1];
char[] b = new char[1];
short[] c = new short[1];
int d[] = new int[1];
long e[] = new long[2];
boolean f [] = new boolean[2];
Integer g = new Integer(3);
Byte h = new Byte((byte) 2);
int[] i = {2, 3,};
String[] j = {"Hi"};
Main[] k = new Main[3];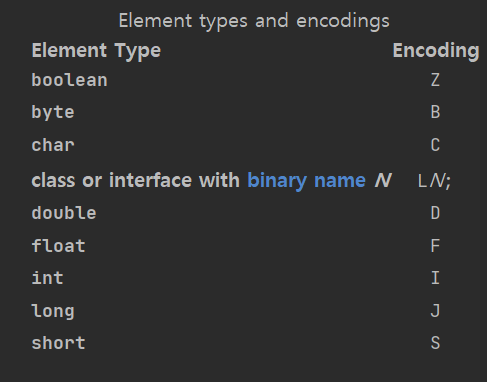

배열의 경우엔 '['가 표시되어 배열이라는 것을 알려준다.
reference type의 경우엔 'L' 다음에 package명.class명으로 표시된다.
그리고 @ 뒤에는 hashCode를 16진수로 변환한 후 String으로 반환한 값이 나온다.